Summary: This guide explains how AI quality control in manufacturing helps leaders move from reactive inspection to proactive defect prevention. It shows how manufacturers reduce scrap, downtime, and compliance risk by using intelligent inspection systems that work in real time across production lines. You learn why traditional quality methods fail, how AI-driven quality control works in practice, where it delivers measurable results, and how to implement it step by step without disrupting operations. Practical challenges, proven solutions, and real examples help decision-makers understand where to start, how to scale, and how to turn quality improvement into sustained business impact.
If you are wondering how does AI enhance quality control in manufacturing? Here’s the answer, AI enhances quality control in manufacturing by making inspections more accurate, consistent, and continuous, even at high production speeds where manual checks begin to fail.
Manufacturing quality has reached a critical point. Global competition, tighter margins, and higher customer expectations are pushing factories to produce more without compromising standards. Yet defects continue to drain billions from the industry every year. Most quality failures do not come from broken machines but from inspection systems that cannot keep up with today’s production demands. Human inspectors struggle with fatigue, inconsistent judgment, and increasing line speeds, leading to missed defects and delayed decisions.
AI Quality Control in Manufacturing changes this reality by embedding intelligence directly into inspection processes. Instead of relying on sampling or periodic checks, manufacturers can inspect every product in real time. Artificial intelligence in quality control ensures that decisions remain consistent across shifts, locations, and product variations. This approach not only improves defect detection but also reduces downtime caused by late-stage rejections.
As manufacturers accelerate digital adoption, AI-driven inspection has become a core pillar of AI in Manufacturing strategies. It aligns quality assurance with automation, data visibility, and operational efficiency goals. Quality is no longer a final checkpoint. With AI, it becomes a continuous safeguard that protects revenue, reputation, and customer trust.
Why do traditional quality control methods struggle in modern manufacturing environments?
Traditional methods rely heavily on human inspection and static rules, which cannot scale or adapt to fast-changing, high-volume production lines.
Manual inspection processes often miss subtle defects, especially surface irregularities, alignment issues, or micro-level faults. Studies consistently show that manual checks can miss up to thirty percent of defects under real production conditions. At the same time, skilled labor shortages make it difficult to consistently staff inspection roles, particularly during night shifts and peak production periods.
Manufacturers face several recurring quality challenges:
- Rising defect rates that lead to recalls, penalties, and brand damage
- Inconsistent inspection results across shifts and facilities
- Production slowdowns caused by quality bottlenecks
- Compliance risks due to incomplete or inconsistent documentation
- Higher costs from rework, scrap, and delayed shipments
These quality gaps often extend beyond the factory floor. Defects discovered late disrupt logistics, inventory planning, and vendor coordination. This is where alignment with AI for supply chain visibility becomes essential, as quality failures often ripple through the entire value chain.
AI Quality Control in Manufacturing addresses these gaps by replacing subjective judgment with data-driven decisions. Inspection systems learn from real production data and adapt as products or materials change. When quality systems fail to evolve, inefficiency becomes embedded in daily operations rather than appearing as an exception.
Did you know that according to industry surveys, a majority of manufacturing professionals report that AI supports production and inspection roles by enhancing accuracy and reducing workload, demonstrating broad confidence in AI-driven systems on the shop floor. (Statista)
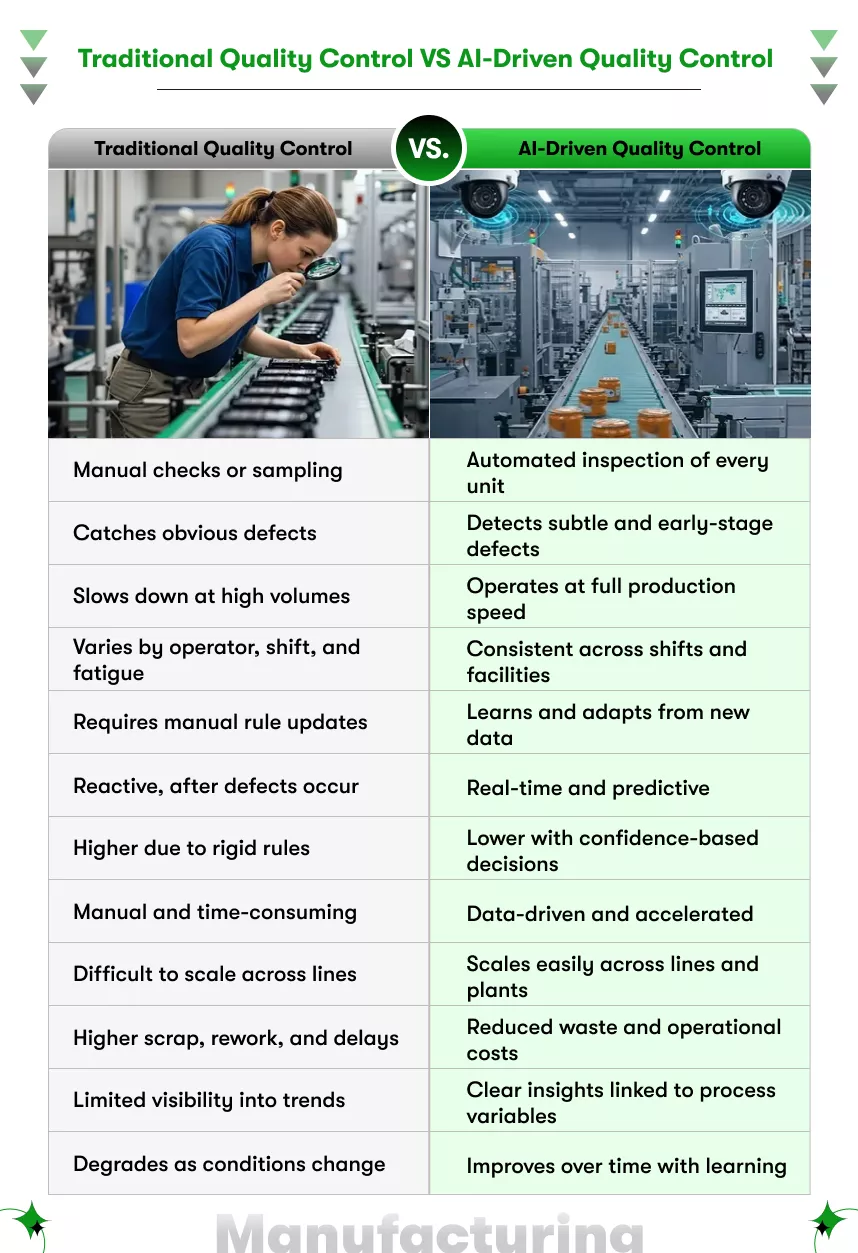
How does AI quality control in manufacturing actually operate on the shop floor?
It captures real-time production data, learns what acceptable quality looks like, and flags deviations instantly without slowing output.
AI-driven quality systems use cameras, sensors, and production data to monitor products as they move through each stage of manufacturing. These systems are trained on historical defect patterns and continuously updated with live production data. Over time, they become better at recognizing both known and emerging defect types.
The workflow typically follows a precise and repeatable path:
- Visual and sensor data are captured continuously from the production line
- The system learns standard quality patterns and defect variations
- Each unit is inspected in real time without interrupting the flow
- Alerts are triggered when deviations occur
- Insights are fed back to operators and engineers for corrective action
Unlike rule-based inspection tools, AI adapts to variations in lighting, materials, and design changes. This makes AI Quality Control in Manufacturing especially valuable for manufacturers handling multiple SKUs or frequent product updates.
When combined with AI in automation, quality decisions can automatically trigger adjustments such as line speed changes or targeted maintenance actions. Intelligent inspection turns quality control into a live feedback loop rather than a reactive gate.
Where is AI quality control in manufacturing already delivering results?
Across automotive, electronics, and food production, AI-driven inspection systems are reducing defects, cutting inspection time, and improving consistency.
In automotive manufacturing, AI vision systems inspect weld seams, surface finishes, and component alignment with high precision. Manufacturers deploying these systems have reported defect reductions exceeding ninety percent in specific processes. This improvement directly reduces recalls and stabilizes production schedules.
In electronics manufacturing, AI in manufacturing quality control identifies micro-level defects on printed circuit boards that are difficult for the human eye to detect. Inspection time has dropped by nearly 70% across several facilities, enabling faster throughput without sacrificing accuracy.
A strong example of AI quality control in the manufacturing industry comes from food and beverage plants, where AI detects contamination, seal defects, and labeling errors in real time. These systems help ensure safety compliance while reducing unnecessary product rejection.
These outcomes reflect broader AI Use Cases in Manufacturing, where quality data feeds directly into cost control, process optimization, and performance improvement initiatives. Proven results across industries confirm that AI-driven quality control is not experimental. It is operational, scalable, and measurable.
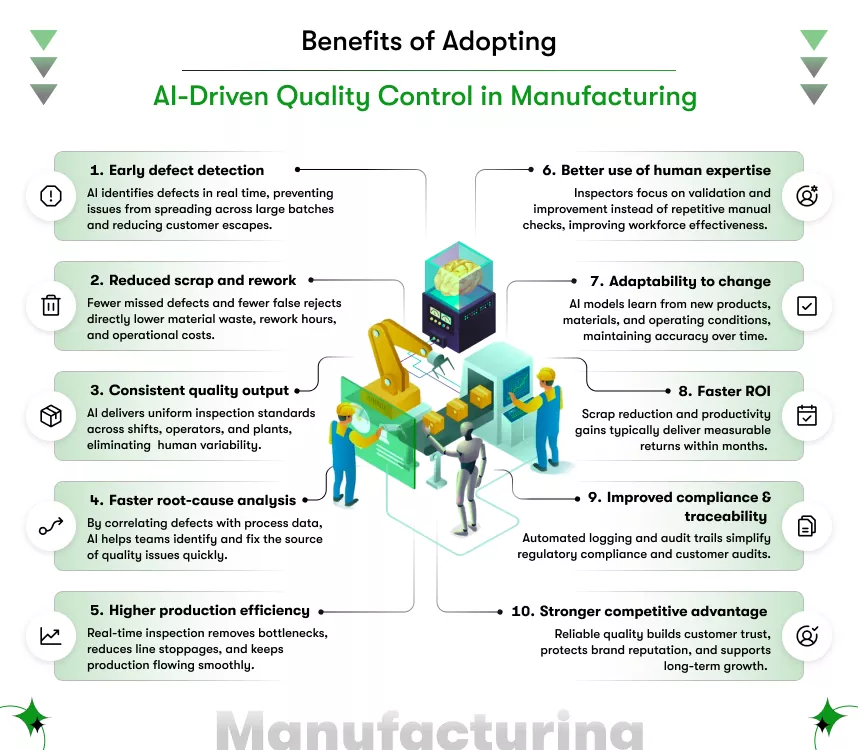
What benefits do manufacturers gain from AI quality control in manufacturing?
They achieve faster inspections, fewer defects, better compliance, and deeper insight into production performance.
AI-driven quality systems deliver benefits that align closely with executive priorities:
- Inspection speed improves without increasing labor costs
- Defect rates fall, reducing scrap and rework expenses
- Production runs with fewer unexpected stoppages
- Audit readiness improves through consistent data capture
- Process insights support continuous improvement initiatives
Manufacturers often recover up to twenty percent of their production budget by reducing quality-related losses. These gains strengthen margins while supporting long-term competitiveness.
These outcomes reinforce broader AI benefits in manufacturing, including operational resilience and improved decision-making. When quality improves consistently, profitability follows naturally.
How can manufacturers implement AI quality control in manufacturing without disrupting operations?
By following a phased approach that focuses on high-impact processes first and scales gradually.
Successful implementation begins with identifying where quality failures cause the most financial and operational damage. This often involves reviewing defect logs, downtime reports, and customer complaints. Instead of deploying AI across the entire plant immediately, manufacturers benefit from piloting solutions on one critical line or process.
A practical implementation roadmap includes:
- Auditing current quality workflows to identify inspection gaps
- Aligning initiatives with ongoing AI manufacturing trends, such as smart factories and connected production
- Selecting tools that integrate with existing MES and automation systems
- Running a pilot project using real production data
- Training teams on interpreting and acting on inspection insights
- Scaling deployment once clear performance improvements are measured
AI quality systems are most effective when paired with AI for Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing, allowing manufacturers to address equipment issues and quality deviations together rather than in isolation.
At Kody Technolab Ltd., our AI Development Services deliver production-ready solutions that integrate with existing workflows and scale with business growth. Thoughtful implementation turns AI quality control from a technology project into an operational advantage.
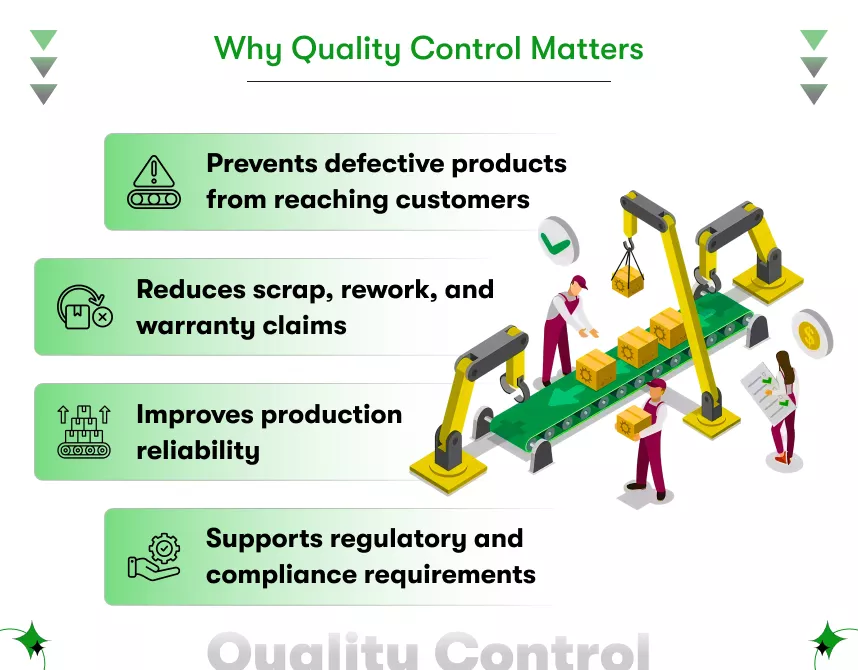
What challenges do manufacturers face when adopting AI quality control in manufacturing, and how can they overcome them?
Manufacturers often worry about data quality, costs, integration complexity, workforce readiness, and measurable returns, but each of these challenges has proven solutions when approached strategically.
Adopting AI Quality Control in Manufacturing is not about replacing existing systems overnight. It is about strengthening quality outcomes step by step while minimizing risk. Below are the most common challenges manufacturers face, along with practical solutions and real-world examples that show how AI delivers measurable impact.
Challenge 1: Inconsistent or Poor-Quality Inspection Data
Many manufacturers believe they lack the clean data required for AI-based inspection. Legacy systems, manual records, and fragmented data sources often create gaps that slow adoption. This concern frequently delays projects before they even begin.
Solution:
AI Quality Control in Manufacturing systems does not require perfect data from day one. Modern inspection models improve through continuous learning. By starting with a focused pilot line, manufacturers can collect structured image and sensor data under real operating conditions. Over time, the system refines defect recognition accuracy as more examples are captured.
Example:
A mid-sized metal fabrication plant struggled with inconsistent defect records across shifts. By deploying AI visual inspection on a single welding line, the company standardized defect data within weeks. Within three months, defect classification accuracy improved by over forty percent, enabling better root-cause analysis and faster corrective action.
Closing perspective: Clean data is not a prerequisite for AI quality control. It is often the outcome.

Challenge 2: High Initial Investment Concerns
Many decision-makers hesitate due to perceived high upfront costs. There is a fear that AI Quality Control in Manufacturing requires significant capital expenditure with unclear payback timelines.
Solution:
Phased deployment reduces financial risk while delivering early wins. Instead of a full-scale rollout, manufacturers can start with one critical process where defects cause the highest losses. Cloud-based inspection models and modular hardware further reduce upfront investment. ROI becomes visible once scrap reduction and throughput improvements are measured.
Example:
An electronics manufacturer piloted AI-based inspection on a single PCB assembly line. The initial investment was recovered in under 6 months due to a 60% reduction in rework costs. After validating results, the system was scaled across additional lines with confidence.
Closing perspective: When deployed strategically, AI quality control pays for itself faster than most traditional automation investments.
Challenge 3: Integration with Existing Production Systems
Factories often run on a mix of legacy equipment, MES platforms, and automation tools. There is concern that AI systems will disrupt existing workflows or require extensive reconfiguration.
Solution:
AI Quality Control in Manufacturing solutions are designed to integrate alongside existing infrastructure. Cameras and sensors are added without interrupting production, while software connects with current dashboards and reporting tools. This allows manufacturers to enhance inspection capabilities without reengineering the entire line.
Example:
A packaging manufacturer integrated AI inspection into an existing conveyor system without modifying equipment layout. Defect alerts were routed directly to the quality dashboard already used by supervisors. This seamless integration reduced response time to quality issues by more than fifty percent.
Closing perspective: AI strengthens existing systems instead of replacing them when integration is planned thoughtfully.
Challenge 4: Workforce Resistance and Skill Gaps
Employees often fear that AI-driven inspection will replace jobs or add complexity to daily tasks. Lack of familiarity with intelligent systems can slow adoption and reduce trust in inspection results.
Solution:
Successful AI Quality Control in Manufacturing implementations focus on augmentation rather than replacement. AI handles repetitive inspection tasks while quality teams concentrate on analysis, decision-making, and improvement initiatives. Simple interfaces and hands-on training help teams adopt the system quickly. In many cases, manufacturers also choose to hire AI Developers with manufacturing experience to bridge internal skill gaps and accelerate deployment without overburdening existing teams.
Example:
A food processing plant introduced AI inspection to monitor packaging integrity. Inspectors were trained to validate AI alerts and investigate root causes rather than manually checking every unit. Within weeks, acceptance increased, and inspection productivity doubled without reducing headcount.
Closing perspective: When teams understand that AI supports their work, adoption accelerates naturally.
Challenge 5: Proving Measurable Business Impact
Executives often ask whether AI Quality Control in Manufacturing delivers real business value beyond technical improvements. Without clear metrics, projects struggle to gain long-term support.
Solution:
Clear KPIs must be defined before deployment. These include defect rate reduction, scrap cost savings, inspection cycle time, and downtime avoidance. AI systems provide continuous performance data that links quality improvements directly to financial outcomes.
Example:
A consumer goods manufacturer tracked defect-related downtime before and after the deployment of AI inspection. Within four months, unplanned stoppages dropped by 30%, resulting in measurable production gains and faster order fulfillment.
Closing perspective: When quality improvements are tied to financial metrics, AI adoption becomes a strategic decision rather than an experiment.
Challenge 6: Scaling AI Quality Control Across Multiple Lines
After a successful pilot, manufacturers often struggle to scale AI Quality Control across products, plants, or regions due to process variability.
Solution:
Scalable AI architectures allow models to be adapted rather than rebuilt. Once core defect patterns are learned, they can be fine-tuned for new lines with minimal retraining. Standardized deployment frameworks accelerate expansion and make it more predictable.
Example:
An automotive supplier expanded AI inspection from one plant to three additional facilities within a year. Because the core model was already trained, deployment time per plant dropped by more than fifty percent, accelerating ROI across operations.
Closing perspective: Scalability is not a barrier when AI systems are designed with growth in mind.
Section Closing Summary:
Every manufacturing transformation faces resistance, uncertainty, and risk. AI Quality Control in Manufacturing succeeds when challenges are addressed with structured planning, realistic expectations, and measurable goals. The result is not just better inspection but stronger operational control, lower costs, and sustained quality excellence.
Where is AI quality control in manufacturing heading next?
Toward deeper integration with automation, maintenance, and real-time decision systems.
Future quality systems will not only detect defects but also predict them by analyzing upstream process data. Integration with robotics and automated handling systems will allow defects to be removed or corrected instantly. These developments align with broader AI in automation initiatives shaping next-generation factories.
Manufacturers that invest early in scalable quality systems will be better positioned to adapt as products, materials, and regulations evolve. The future of quality control lies in prevention, not inspection alone.
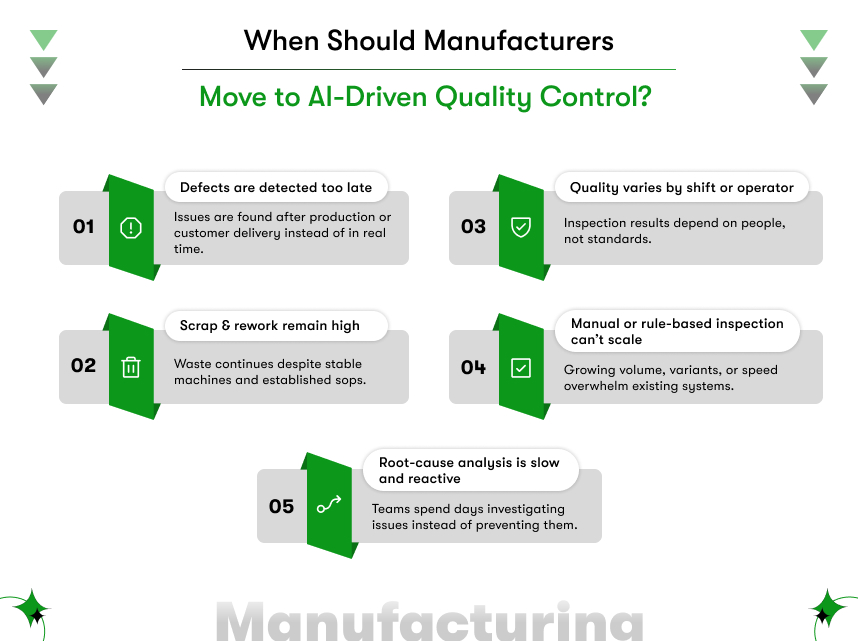
Why should manufacturers act now on AI quality control in manufacturing?
Because quality losses compound quietly while competitors gain efficiency through intelligent systems.
AI Quality Control in Manufacturing transforms inspection from a reactive task into a proactive capability. It reduces defects, stabilizes operations, and strengthens customer trust. For manufacturers facing rising costs and shrinking margins, the impact is immediate and measurable.
As AI continues reshaping production environments, quality control stands out as one of the fastest ways to achieve tangible returns. Ready to modernize your quality strategy? Connect with Kody Technolab Ltd. to explore AI-driven quality solutions designed for real manufacturing challenges.

FAQ
1. Is AI quality control only viable for large manufacturing plants?
No. Scale helps, but it’s not the deciding factor. What matters more is repeatability and cost of defects. Even mid-sized manufacturers benefit if a single defect type is causing scrap, rework, or customer risk. AI Quality Control in Manufacturing pays off fastest where defects are frequent, expensive, or hard to catch manually.
2. How long does it realistically take to see ROI from AI-driven quality control?
If the use case is chosen correctly, measurable impact often shows up within 3–6 months. Scrap reduction and false reject reduction are usually the first wins. Projects that take a year to prove value are usually over-scoped or poorly aligned with operations.
3. Does AI replace human quality inspectors?
No, and it shouldn’t. AI replaces repetitive inspection tasks, not judgment. Inspectors shift from staring at parts to validating exceptions, investigating root causes, and improving processes. Plants that position AI as “replacement” struggle with adoption. Plants that position it as support succeed.
4. What happens when products, materials, or processes change?
Change is normal in manufacturing. AI systems must be designed to adapt. That means retraining models as new variants are introduced and continuously learning from fresh production data. If a vendor can’t explain how they handle change, the system will degrade over time.
5. How reliable are AI decisions in audits or customer disputes?
Reliable if traceability is built in. Strong AI quality systems log inspection results, confidence scores, and decision rationale. That audit trail matters for compliance, recalls, and customer escalations. If you can’t explain why a defect was flagged or missed, the system isn’t enterprise-ready.
6. What’s the biggest mistake manufacturers make when adopting AI quality control?
Starting with technology instead of a problem. Successful AI Quality Control in Manufacturing Industry initiatives begin with a clear defect, a clear cost, and a clear success metric. Tools come later. When teams skip that step, AI becomes an experiment instead of an operational asset.












 Contact Information
Contact Information