Quick Summary: Healthcare leaders who plan to develop an AI-powered EHR system can use this guide to understand every major step of the journey. The blog explains how AI supports clinical workflows, which features create real value, what technology stack fits modern healthcare, how development costs are structured, and how in-house and outsourced teams differ. Readers gain clear, practical knowledge to plan budgets, evaluate options, and build an EHR system that meets clinical and operational objectives.
If you plan to develop an AI-powered EHR system that lowers cost and lifts margins, start here. Electronic Health Records promised a paperless clinic. Instead they delivered copy-paste overload, 3 a.m. charting marathons and a 14 percent burnout spike.
Artificial Intelligence is the first technology proven to reverse that trend. Early-adopter hospitals cut documentation time 38 percent and reclaimed 1.2 million dollars per 100 providers in the first 12 months. (Source: Deloitte)
The chequebooks are already open.
– Health systems >$10 B revenue are pouring ≥$50 M into AI projects.
– Mid-size players ($5–10 B) are earmarking <$50 M just to keep up.
One driver: CMS will raise Medicare reimbursements 1.88 percent in 2025 for clinics that reach “substantial” AI-use thresholds. Every quarter you delay is cash left on the table.
If you are planning a new EHR build or want to retrofit AI into an existing platform, this guide gives you the feature stack, tech choices, compliance checklist and cost model we use to ship HIPAA-compliant, AI-ready EHRs in 120 days.
Take the next 90 seconds to read this guide and you will leave with a clear, step-by-step vision on how to develop an AI-powered EHR system and uncover the potential and possibilities of AI in healthcare.
What is an EHR system?
An Electronic Health Record (EHR) system stores patient information such as medical history, vitals, medications, and diagnostic data in one secure digital place. This foundation becomes essential when you plan to develop an AI-powered EHR system, since AI relies on accurate and structured data.
EHRs reduce documentation errors, support faster clinical decisions, and improve coordination between care teams. Unlike EMRs, EHRs are built for interoperability, enabling smooth data sharing across hospitals, specialists, labs, and external systems.
Countries like the Netherlands show how strong digital records and clean data architecture make advanced features and AI-powered EHR software development easier to adopt.
Dutch e-health leaders like ChipSoft show how digital healthcare transformation succeeds only when technology decisions align with an organization’s long-term clinical and operational goals.
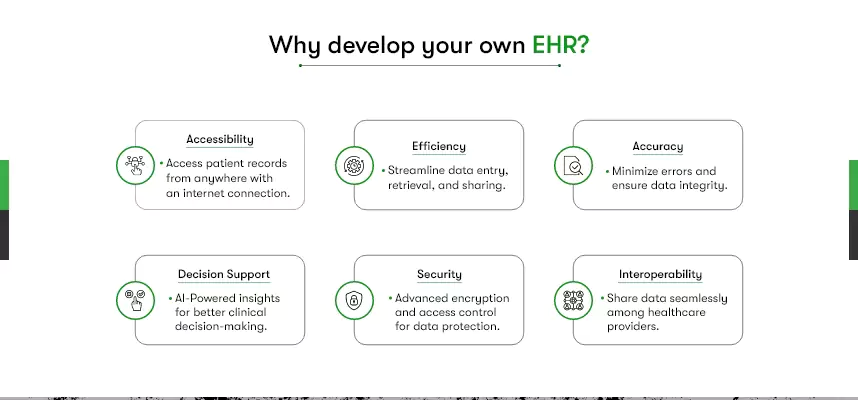
Why develop your own EHR?
- Accessibility: Access patient records from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Efficiency: Streamline data entry, retrieval, and sharing.
- Accuracy: Minimize errors and ensure data integrity.
- Decision Support: AI-powered insights for better clinical decision-making.
- Security: Advanced encryption and access control for data protection.
- Interoperability: Share data seamlessly among healthcare providers.
If you plan to develop an AI app and don’t know where to start, our AI app development guide will walk you through every step.
How is AI used in EHR?
Artificial Intelligence enhances Electronic Health Records (EHR) by improving accuracy, reducing manual workload, and supporting faster clinical decisions. AI models analyze structured and unstructured patient data, identify patterns, and generate insights that improve daily workflows. These capabilities form the core of modern platforms built when you develop an AI-powered EHR system.
Clinical Decision Support:
AI-powered EHR systems help doctors make better decisions by analyzing patient data and providing insights. For example, they can suggest the most suitable treatment options or predict patient outcomes based on historical data.
Medical Image Analysis:
AI algorithms can analyze medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. They can quickly detect anomalies, tumors, or fractures, assisting radiologists and clinicians in making accurate diagnoses.
For example, aidoc’s ai platform aids radiologists by swiftly detecting abnormalities in medical imaging scans, ensuring faster and more precise diagnoses.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP converts unstructured clinical notes into searchable, structured data. This improves documentation quality, speeds up information retrieval, and strengthens AI-powered EHR software development by making data more usable.
For example, Natural Language Processing (NLP) can transform unstructured medical notes into structured EHR data, streamlining healthcare record management.
Predictive Analytics:
AI can learn from data to predict disease outbreaks, patient readmissions, or potential adverse events. This enables healthcare providers to take preventive measures and improve patient outcomes.
Personalized Treatment Plans:
Understanding the patient’s medical history recorded in the EHR system, AI can help healthcare professionals provide tailored treatment plans.
Administrative Automation:
AI automates administrative tasks within EHR systems, such as appointment scheduling and billing. This reduces errors, saves time, and allows healthcare staff to focus on patient care.
Olive’s AI Workforce is setting the best example by automating administrative tasks, including EHR-related paperwork, reducing administrative burdens for healthcare professionals.
Voice Recognition:
EHR systems equipped with AI can transcribe doctor-patient conversations accurately. This eliminates the need for manual note-taking and improves documentation.
Take Nuance Communications’ Dragon Medical One, for example. It employs AI-driven voice recognition to transcribe doctor-patient conversations directly into EHRs, improving documentation efficiency.
Medication Management:
AI plays a vital role in avoiding medication errors by cross-referencing a patient’s prescribed medications and medical history. This proactive approach reduces the chances of harmful drug interactions.
Population Health Management:
AI identifies groups at higher risk of chronic conditions and helps organizations design targeted intervention programs.
For Example: Optum’s population health platform analyzes EHR datasets to find patterns in chronic disease progression and support large-scale preventive care strategies.
Each AI capability enhances the reliability, efficiency, and intelligence of EHR systems. As healthcare providers evaluate how to develop an AI-powered EHR system, these examples show how the right data architecture and model integration can significantly improve care delivery.
How to innovate your EHR Features using Artificial Intelligence?
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence in EHR system development allows healthcare organizations to build smarter, more efficient, and more proactive digital systems. AI-driven features improve workflow accuracy, reduce operational load, support clinical decisions, and unlock meaningful insights from patient data.
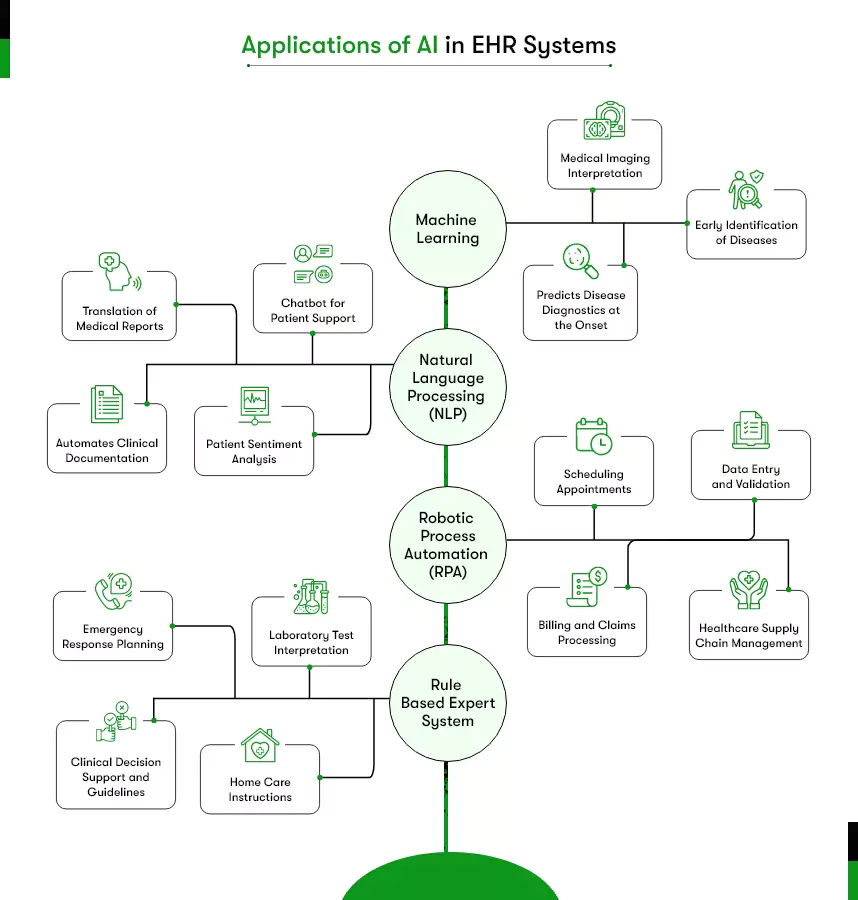
These capabilities become especially important when you plan to develop an AI-powered EHR system, as AI determines how well the platform can scale and support future care models. Below are the key AI features you can integrate into your EHR.
Clinical Decision Support (CDS):
AI-powered CDS provides real-time recommendations and alerts to healthcare professionals based on patient data, assisting with diagnosis and treatment decisions. That would otherwise take significant time with a traditional EHR system.
Disease Progression:
AI models can evaluate patient history, vitals, clinical notes, and lab trends to predict the likelihood of disease progression. This helps healthcare teams identify at-risk patients, plan timely interventions, and improve long-term outcomes. Predictive capabilities like these bring measurable value across hospitals and specialty practices.
Structured Data Creation
Using Natural Language Processing (NLP), AI can convert unstructured clinical notes into structured, standardized fields. This strengthens documentation accuracy, improves searchability, and ensures cleaner datasets for advanced analytics and future AI-powered EHR software development.
Automated Documentation:
AI combined with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) supports automated clinical documentation. It captures information from clinical workflows, organizes it, and populates relevant fields within the EHR. This reduces administrative burden and minimizes documentation gaps.
Chatbot for Patient Engagement:
AI-driven chatbots can assist patients with appointment scheduling, medication-related questions, follow-ups, and general information. A personalized virtual assistant improves patient experience and reduces inbound call volume for staff.
Security and Privacy Enhancement:
AI strengthens data security by monitoring access and identifying potential security threats, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations. Hence, you can focus on implementing robust security measures and protecting patient data, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
Drug Recommendations:
AI can suggest the most appropriate medications and dosages by analyzing the patient’s historical data and following clinical guidelines.
Administrative Operations:
AI can automate recurring administrative tasks such as insurance verification, appointment management, coding assistance, and form processing. Automating these workflows improves operational efficiency and frees staff for higher-value tasks.
Patient Portal:
To elevate the patient experience with healthcare organizations, you can allow them to access their records, appointment scheduling, and secure communication with a tailored portal.
Interoperability:
An EHR needs to support data sharing and interoperability with other healthcare systems to promote seamless information exchange.
AI-led enhancements allow an EHR to perform faster, support better decisions, and handle complex workflows with precision. This foundation becomes essential for any team preparing to develop an AI-powered EHR system.
What Technology to Use to Develop an AI-Powered EHR System?
AI-powered EHR software development requires a technology stack that supports secure data handling, fast performance, interoperability, and advanced AI workloads. Choosing the right stack becomes especially important when teams plan to develop an AI-powered EHR system because both clinical and operational functions depend on reliable architecture.
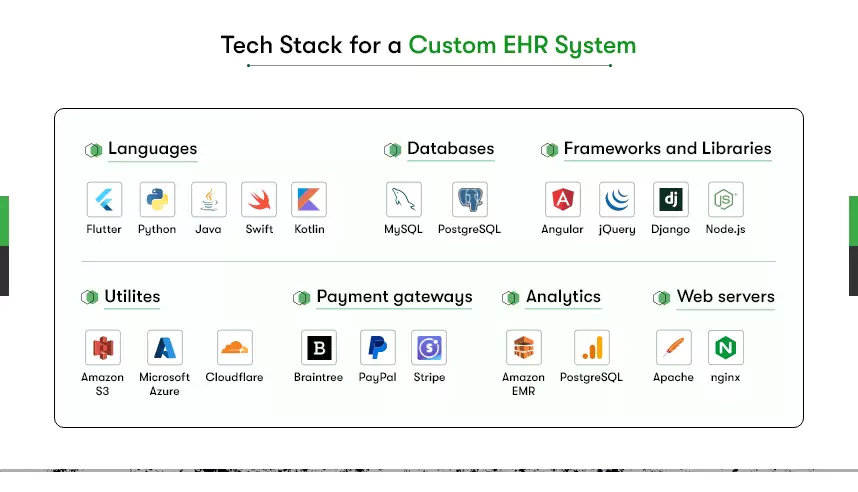
A complete EHR tech stack generally includes backend frameworks, frontend technologies, AI and machine learning libraries, interoperability standards, cloud services, and secure storage systems. Each part plays a specific role in ensuring the EHR remains compliant, scalable, and capable of handling structured and unstructured healthcare data.
Backend Technologies
Robust backend technologies such as Python, Java (Spring Boot), Node.js, and .NET help manage API communication, authentication, role-based access, and integration with hospital systems. These languages support HIPAA-compliant implementations and allow smooth data flow across clinical modules.
Databases and Storage
Healthcare data requires reliable databases such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, and cloud object storage for files, imaging, and logs. Structured and unstructured data support is essential for AI features and analytics.
AI and Machine Learning Frameworks
AI functions in EHRs often require tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, spaCy, and ONNX. These frameworks power clinical decision support, NLP, medical imaging analysis, predictive analytics, and workflow automation features.
Interoperability and Standards
EHR systems must connect seamlessly with HIS, LIS, RIS, PACS, labs, pharmacies, and third-party platforms. Standards such as HL7, FHIR, CDA, and RESTful APIs ensure smooth information exchange and reduce integration delays.
Cloud and DevOps Infrastructure
Platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure support HIPAA-ready hosting, encryption, auto-scaling, and monitoring. Kubernetes, Docker, Terraform, and CI/CD pipelines help maintain stability, manage updates, and support continuous model deployment for AI features.
Frontend and Cross-Platform Development
Healthcare organizations often prefer a consistent interface across mobile, tablet, and web platforms. Flutter supports responsive web applications, Android apps, and iOS apps from a single codebase, which makes it a strong choice for cross-platform app development in modern EHR projects. Teams working with Flutter need experience in Dart, secure storage practices, encryption standards, and healthcare-focused UI design to ensure compliance and smooth user experience.
Specialized Mobile Development
Developers working on mobile versions must understand HIPAA compliance, secure session handling, offline data rules, and integration of AI-driven components inside mobile workflows.
A well-planned technology stack supports system performance, compliance, scalability, and long-term maintainability. Strong technical foundations help organizations move confidently into the next stages of AI-powered EHR software development, especially when combining modern backend frameworks with reliable options like Flutter for healthcare app development, which supports consistent, secure, and scalable experiences across platforms.
How much does EHR software Development cost?
The cost to develop an AI-powered EHR system generally ranges from USD 30,000 to USD 70,000, depending on scope, complexity, features, integrations, and compliance requirements. Healthcare organizations invest at different levels based on whether they need a basic clinical module or a fully AI-enabled platform with advanced automation and predictive intelligence.
The table below provides a clear overview of typical cost allocation for AI-powered EHR software development.
EHR Development Cost Breakdown
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost Share | What It Covers |
| Scope & Complexity | 15% – 20% | Requirement analysis, technical specification, user roles, workflow design |
| Features & AI Functionality | 20% – 25% | Core EHR modules, AI engines, predictive models, NLP features, CDS |
| Customization | 10% – 15% | Organization-specific workflows, specialty modules, custom dashboards |
| Regulatory Compliance | 10% – 15% | HIPAA requirements, encryption, audit logging, secure access controls |
| Data Integration | 10% – 15% | Integration with HIS, LIS, RIS, PACS, lab systems, APIs, FHIR/HL7 |
| UI and UX Design | 5% – 10% | User journeys, interface design, navigation flows, accessibility standards |
| Testing & Quality Assurance | 10% – 15% | Functional, security, performance, penetration testing, AI model validation |
| Deployment & Maintenance | 10% – 15% | Release cycles, cloud setup, continuous updates, model monitoring |
These ranges represent common allocations and can shift based on project size, AI depth, or integration volume.
Additional Cost Factors to Consider
When planning the budget to develop an AI-powered EHR system, the following elements also play a significant role:
1. AI Integration Depth
Costs depend on whether you require:
- Basic automation
- NLP-based note structuring
- Predictive analytics
- Imaging analysis
- Advanced clinical decision support
More AI layers increase workload for data engineering and model development.
2. Data Migration
Migration from legacy systems often requires cleaning, mapping, standardizing, and validating existing records. Effort increases when data is unstructured or spread across multiple systems.
3. Infrastructure and Cloud Hosting
Costs vary based on:
- AWS, Azure, or GCP hosting
- HIPAA-ready cloud environments
- Storage for files, logs, and medical images
- Load balancing, backups, monitoring, and scaling
4. Security Enhancements
Includes:
- Role-based access
- Multi-factor authentication
- Encryption
- Audit trails
- Threat detection using AI
Healthcare data demands higher security investment compared to typical SaaS systems.
5. Integrations with External Systems
Additional development may be required for:
- HL7/FHIR mapping
- Lab systems
Pharmacy systems - Insurance platforms
- IoT and medical devices
6. Post-launch AI Model Monitoring
AI requires:
- Ongoing validation
- Performance tracking
- Data drift monitoring
- Regular updates to maintain accuracy
7. Team Expertise
Cost varies based on seniority and specialization:
- AI/ML engineers
- Backend developers
- Flutter developers for mobile interfaces
- DevOps engineers
- Compliance specialists
A clear understanding of these components helps healthcare teams allocate budgets effectively and prepare realistic timelines. Every organization planning to develop an AI-powered EHR system will have unique needs, so the final cost depends on the depth of features, AI capabilities, and integration requirements.
How to Develop an EHR System That Meets Modern Healthcare Standards
Developing an Electronic Health Record system requires structured planning, clinical workflow understanding, and strict compliance. The focus is to create a secure, interoperable, and AI-ready platform that supports clinicians without interrupting routine care. Any organization planning to develop an AI-powered EHR system can follow the steps below or collaborate with an experienced healthcare app development company for technical clarity and execution.
When hiring, if relevant, prioritize developers with experience in healthcare software, HIPAA compliance, and AI integration.
Concept Validation: Choosing the Right EHR Type
First, let’s clarify the type of EHR system you need. There are various types, such as Ambulatory EHR (for clinics), Inpatient EHR (for hospitals), and Specialty EHR (for specific medical practices).
Carefully assess your healthcare organization’s requirements to select the most suitable type. Typically, EHR systems are built by custom software development teams that include engineers, healthcare professionals, and data experts.
Discovery and Prototypes: Setting the Foundation
In the discovery and prototype phase, lay the groundwork for your EHR system development. This stage involves in-depth research and planning to define project goals, user needs, and system requirements.
To visualize how the EHR will work, create prototypes and mockups. These visuals help ensure that the system aligns with the workflow of healthcare professionals, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
Design and Development: Bringing Your AI-powered EHR to Life
During the design phase, your skilled designers focus on crafting a user-friendly interface. Ensure prioritizing ease of use and accessibility of your EHR, keeping healthcare professionals in mind.
Simultaneously, software engineers work on building the EHR system itself. This also includes developing and integrating AI algorithms and features. For example, incorporate AI algorithms for tasks like predictive analytics, natural language processing (NLP), and image recognition.
It’s a crucial step to ensure your EHR functions seamlessly and complies with industry standards and regulations.
Debug and Launch: Ensuring a Smooth Takeoff
After development, rigorous testing and quality assurance take center stage. This phase is vital to ensure data accuracy, security, and system reliability. Once the EHR system is thoroughly tested and free of any issues, it’s time to launch your EHR.
After the launch, monitor the system, address emerging issues, and adapt to evolving healthcare needs.
As you develop your EHR system, remember that each stage plays a pivotal role in creating a dependable and efficient healthcare solution. Therefore, outsourcing to experienced developers can make this journey smoother, ensuring that your EHR meets the unique demands of your healthcare organization.
Collaboration with an established AI development company often helps teams move through the process with clarity while ensuring the system fits their clinical and operational demands.
In-house vs Outsourced EHR Development: What’s Practical?
Healthcare teams often evaluate whether to build an Electronic Health Record system internally or partner with an external healthcare app development company. Each option affects cost, delivery speed, compliance readiness, and long-term maintainability. A structured comparison helps organizations choose the approach that fits their capabilities.
In-house EHR Development
Developing an EHR internally gives organizations full ownership of the system and complete control over development decisions. Internal teams understand existing workflows and operational routines, which helps shape features that support daily clinical practices.
Key strengths of in-house development include:
- In-house teams maintain direct communication with clinicians, which helps ensure that every feature reflects actual clinical workflows.
- Organizations control all security and data-handling processes, which offers stronger decision-making authority over sensitive patient information.
- Internal development teams can align system enhancements with operational changes without depending on external resources.
However, in-house development also requires significant long-term investment:
- Organizations need to hire and retain developers with expertise in healthcare standards, AI capabilities, security frameworks, and clinical-grade software development.
- Teams must gain advanced knowledge of HL7, FHIR, HIPAA, authentication protocols, and other interoperability requirements.
- Internal staff must manage infrastructure, server monitoring, quality assurance, and software updates for the entire lifecycle of the EHR system.
This option is suitable for teams that already have strong technical capacity and long-term resources to support AI-powered EHR software development.
Outsourced EHR Development
Outsourcing accelerates development because teams gain immediate access to specialists who already work with EHR systems, clinical workflows, interoperability standards, and healthcare compliance. This option helps reduce risk and shortens timelines for teams exploring how to develop an AI-powered EHR system without building an internal technical department.
Benefits of outsourcing include:
- External teams bring proven experience with AI integration, HIPAA compliance, and interoperability frameworks, which helps reduce development errors.
- Outsourcing provides faster prototyping, quicker feature delivery, and shorter testing cycles due to established workflows and technical expertise.
- Partnering with an external team reduces hiring and training costs because the required skills are already available within the development company.
- Established delivery processes improve predictability in project planning, timelines, and resource allocation.
Important considerations when outsourcing:
- Internal healthcare teams still need to validate clinical workflows to ensure accurate feature development.
- Clear communication practices and structured project governance help maintain alignment between developers and clinical stakeholders.
- Healthcare organizations need to participate in regular reviews to confirm that the evolving system reflects their operational goals.
Outsourcing is often preferred when teams need fast delivery, predictable outcomes, and deep experience in AI in electronic health records development.
Which EHR Development Approach Fits Your Organization?
The right choice depends on team capacity, timeline expectations, and project complexity. Leaders can evaluate their readiness using the following questions:
- Does the internal team have experience with EHR workflows, healthcare requirements, and AI models?
- Can the organization manage long-term maintenance, security updates, and AI model monitoring?
- Is the timeline strict, or can the organization wait while building internal expertise?
- Will the EHR require advanced analytics, clinical decision support, or NLP features?
- Can the internal team manage complex interoperability setups with HIS, LIS, RIS, or PACS systems?
Organizations with strong engineering teams may choose internal development, while teams that need speed, compliance accuracy, or advanced AI capabilities often turn to outsourcing and hire AI developers who bring the required expertise.
A clear assessment of technical expertise, clinical needs, and long-term expectations helps teams choose the development approach that supports stable performance and sustainable growth when they plan to develop an AI-powered EHR system.

Why Kody Technolab for EHR software development?
Selecting the right partner for your EHR software development is paramount, and Kody Technolab offers unparalleled expertise in this domain. We are well-versed in crafting EHR solutions that precisely match your healthcare organization’s needs. Our proficiency extends to leveraging Flutter, a cutting-edge cross-platform framework, ensuring seamless functionality across all platforms.
Security and compliance are at the forefront of our priorities. We meticulously adhere to HIPAA regulations, guaranteeing the utmost patient data protection. What truly distinguishes us is our commitment to customization. From initial concept to post-launch support, we provide comprehensive assistance, including the seamless integration of AI-driven features to enhance patient care.
FAQs
1. What internal information should my healthcare organization prepare before starting AI-powered EHR development?
Healthcare teams should prepare workflow diagrams, user role lists, specialty-specific documentation needs, current system limitations, integration requirements, and compliance expectations. This information helps development teams design accurate features that match real clinical processes.
2. What clinical departments benefit the fastest from an AI-powered EHR system?
Departments with high documentation load or constant data review see the fastest impact. Examples include emergency care, radiology, cardiology, internal medicine, pediatrics, and specialty clinics that rely on structured history, imaging data, and medication records.
3. How does AI improve the accuracy of clinician documentation inside an EHR?
AI improves documentation accuracy through NLP models that convert clinical notes into structured data, voice recognition tools that reduce typing errors, and intelligent prompts that alert clinicians when information is incomplete or inconsistent.
4. Will existing medical devices integrate with an AI-powered EHR system?
Most modern medical devices can integrate with an AI-powered EHR system through standardized communication protocols, secure APIs, and data formats such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM. Integration feasibility depends on device compatibility, available documentation, and the vendor’s support for data exchange.
5. How much data is required to train AI features inside an EHR?
AI components require structured and clean datasets such as patient histories, clinical notes, lab results, imaging data, and medication records. Larger datasets improve accuracy, but even moderate datasets can support useful AI features when processed correctly.
6. Will an AI-powered EHR slow down clinical workflows or speed them up?
AI features generally reduce workload because they automate documentation, highlight missing details, organize patient summaries, and support faster decision-making. A well-designed system speeds up clinical routines rather than slowing them down.
7. Do we need an internal technical team even if we outsource EHR development?
A small internal team is still needed to review workflows, validate clinical logic, provide domain knowledge, and support change management. Outsourcing reduces the technical burden, but internal oversight ensures the system meets clinical expectations.
8. How can we avoid disruptions when switching from an old EHR to a new AI-powered EHR?
Transition planning includes phased rollout, data cleansing, structured migration, parallel system operation, and clinician training. These steps allow teams to shift to the new EHR without interrupting patient care.
9. What compliance risks should healthcare leaders plan for during development?
Leaders must prepare for HIPAA-related requirements such as encryption, access control, audit logs, secure data transfer, and regular testing. AI models also require validation to ensure safe and ethical data processing.
10. How long does it take to see value from AI-driven EHR features?
Most organizations begin seeing value within the first few months after deployment. Improvements include faster documentation, error reduction, better decision support, and clearer insights into patient risk patterns.
11. What factors determine whether in-house development or outsourcing is the better choice?
The right choice depends on internal technical capacity, available clinical involvement, project timelines, and the complexity of AI features needed. Teams with strong engineering resources may choose internal development, while teams that need faster delivery or deeper technical expertise often prefer outsourcing.












 Contact Information
Contact Information