Picking the right flutter database can feel tricky, but it makes or breaks your app’s success. This guide walks you through database types, key selection criteria, performance and compliance factors, and real-world options so you can build secure, fast, and scalable apps with confidence.
Deciding on a flutter database is more than comparing checklists. Picture launch day: thousands of users log in, screens start lagging, orders hang mid-process, and compliance questions surface from investors. That’s the scenario every founder or CTO dreads.
A poor database decision means rewrites, cost overruns, and endless delays. The right foundation, however, keeps your app fast, secure, and ready to grow.
Founders, CTOs, product leads, and agencies need a decision that survives growth and audits. According to Statista, in October 2024, Appfigures counted 727 Flutter apps earning $10,000 to $100,000 each month.
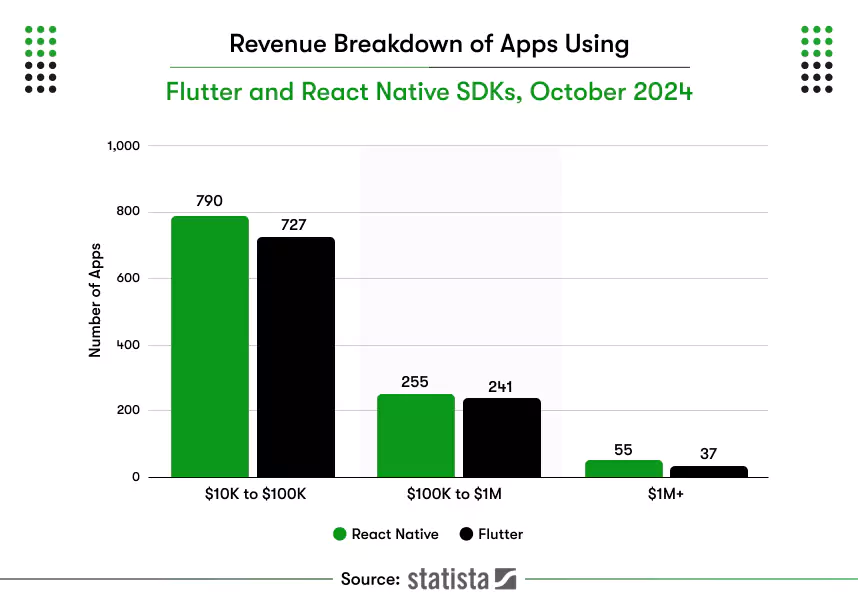
That range reflects steady releases supported by storage choices that match real workloads. Teams in the USA, UK, and UAE also expect encryption, clear logs, and simple retention rules.
Use five checks to validate the fit: data shape, realtime updates, offline behavior, security, and cost. Run small tests to compare Drift with SQLite, Firebase, Isar, and Realm. This method helps teams identify the best database for Flutter without risky rewrites.
Keep reading; this guide turns real product needs into a dependable choice you can ship when building cross-platform applications.
What is a database?
In general, a database is a storehouse of collected data that can be accessed electronically from any device. The data stored can be accessed, modified, updated, controlled, and organized as per the requirements.
The app-focus trend demands real-time data delivery, which means the search query data should be the latest, updated every time it is requested by the end-users. If the application fails to do so, the ball goes into someone else’s court. Well, you can not miss out on an opportunity to impress users with your Flutter app, can you?
And therefore, if you cannot decide on the database, you must take advice from a Flutter app development company. An experienced Flutter development company possesses an eagle eye to analyze the app requirements and suggest the best database.
Now that you know what Databases are, let us see what types of Databases are there to choose from for your Flutter mobile apps.
What is a flutter database, and when should teams use it?
A flutter database stores and retrieves structured app data on device or cloud. Use it to persist state, work offline, sync users, and query quickly. Pick it when reliability, predictable queries, and consistent performance matter across mobile, web, and desktop.
A flutter database can be local or cloud based. Local databases live on the device and work offline. Cloud databases live on managed servers and sync data in real time. Many teams combine both for speed and collaboration.
When should teams use a local, cloud, or hybrid flutter database?
- Choose local storage for fast reads and full offline access.
- Choose cloud storage for multi-user updates and centralized security.
- Use both when apps need offline speed and shared data.
- Pick relational engines for structured entities and joins.
- Pick object or key-value stores for simple documents and caches.
Local storage delivers offline speed and full device control. A managed backend supports realtime collaboration and web parity. When both requirements matter, use a hybrid flutter database with background sync and documented conflict resolution.
Types of Databases for Flutter Mobile App Development
A flutter database comes in two types: relational and non-relational. Use relational for structured tables and transactions. Use non-relational for flexible schemas and realtime sync. Decide using data shape, offline needs, target platforms, team skills, security, and cost today.
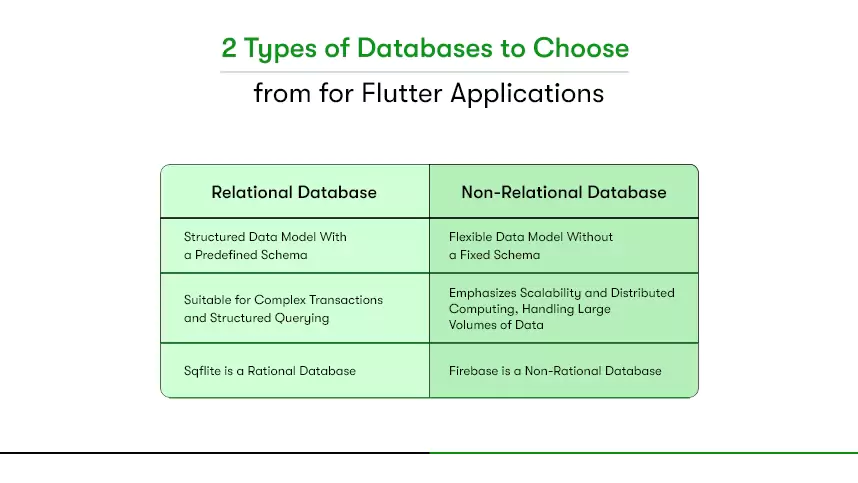
Relational Databases (SQL)
Relational databases store data in tables with fixed schemas. They support joins, constraints, and transactions for reliable consistency. These systems fit structured business records and predictable queries.
- Pick for structured entities, reports, and strict consistency.
- Use when joins, indexes, and transactions matter.
- Works well for analytics and back-office workflows.
- Typical local choice: SQLite with Drift in Flutter apps.
- Typical cloud choice: Postgres or MySQL with an API layer.
- Schema changes require planned migrations and testing.
- Strong fit for compliance and audited data trails.
- Confirm web and desktop needs before finalizing tools.
Non-relational database/NoSQL:
NoSQL databases use flexible models like document or key-value stores. They excel at rapid writes, large datasets, and realtime updates. These systems reduce schema friction during iterative development.
- Pick for documents, events, and fast local caching.
- Use when the schema changes often during growth.
- Great for chat, feeds, and live collaboration.
- Typical local choices: Hive, Isar, or ObjectBox.
- Typical cloud choices: Firestore, Realtime Database, or MongoDB.
- Plan conflict handling for multiuser edits.
- Add rules, encryption, and backups from day one.
- Validate costs under expected read and write patterns.
Relational fits structured entities and formal reporting. NoSQL suits flexible models and realtime collaboration. If both goals matter, use a hybrid with background sync. This approach helps you evaluate the best database for mobile apps while staying aligned with project goals and timelines.
What criteria ensure the right flutter database for your app?
The right flutter database depends on data structure, size, speed, modeling, security, and platform support. Matching these criteria to your project goals avoids rework, improves performance, and ensures your app scales securely across Android, iOS, web, and desktop.
1) Structure of your data
Every app handles data differently. Some need strict tables, while others work with flexible documents. Clarify if your app must store information on-device for offline use or rely on a server for realtime sync.
Key checks
- Map how information is stored and retrieved.
- Decide between local, cloud, or hybrid storage.
- Define rules for data conflicts and exports.
2) Size of the data
Applications that manage customer profiles, media files, or transactions often handle huge volumes. Larger datasets demand stronger storage and faster retrieval strategies.
Key checks
- Estimate total records and expected growth.
- Check partitioning and sharding support.
- Verify how backups and restores are managed.
3) Speed and scale
Performance issues can ruin user experience. High read and write loads need databases designed to maintain speed at scale.
Key checks
- Test average and peak query speeds.
- Profile data-intensive screens.
- Measure battery impact during sync.
4) Data modeling
Poor data modeling leads to complex queries, app crashes, and spiraling costs. The database you select must match how your business processes data and how fast those structures may evolve.
Details to check
- Verify if you need full-text search support.
- Check if location features require geo-queries or spatial indexes.
- Keep models simple and flexible to adapt with growth.
- Document schema evolution to manage migrations safely.
5. Data security:
Security failures destroy customer trust and attract legal penalties. A flutter database must provide strong safeguards that match regulations in your target markets.
Details to check
- Ensure encryption in transit and at rest.
- Review authentication, roles, and fine-grained access rules.
- Enable activity logging for audits and monitoring.
- Confirm compliance with SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, or PDPL standards.
6) Support for multiple platforms
Flutter apps target Android, iOS, web, and sometimes desktop. Your database must support all of them reliably.
Details to check
- Verify SDK maturity for mobile, web, and desktop.
- Test offline capabilities on each target platform.
- Ensure CI/CD pipelines can run automated database tests.
- Confirm consistent API behavior across all supported devices.
Applying these six criteria ensures you don’t select a database blindly. Instead, you evaluate performance, growth, and compliance risks upfront. This disciplined approach helps you shortlist the best database for mobile apps and move toward a reliable Flutter build.
What are the best database options for Flutter apps in 2025?
A flutter database helps apps store, query, and sync data. The best options include SQLite with Drift for structured models, Hive, Isar, or ObjectBox for fast local NoSQL, and Firestore or Supabase for realtime cloud sync across multiple platforms.
SQLite / Drift (Relational)
SQLite is a relational database, and Drift builds on top of it to provide reactive APIs and safer queries. This combination is strong when you need structured data with relationships and want to keep everything offline.
- Works best for apps requiring transactions, joins, and schema validation.
- Allows predictable queries and smooth migrations with version control.
- Supports offline functionality, which many mobile apps need.
- Suitable when teams are comfortable with SQL syntax.
Recommended when:
SQFlite is the best database for mobile apps when you need rational data with control over queries and can write your own queries.
Hive, Isar, and ObjectBox (Local NoSQL)
These databases provide fast local storage using object and key-value models. They are often considered the best database for mobile apps that don’t rely on heavy joins.
- Hive is simple to set up and great for lightweight caching.
- Isar focuses on performance, with indexes for speed on large datasets.
- ObjectBox includes built-in sync, making hybrid architectures easier.
- All three reduce latency and power drain for offline apps.
Firestore and Realtime Database (Cloud NoSQL)
Firestore and Realtime Database from Firebase make data instantly available across devices. They are good when collaboration, realtime updates, and web parity matter most.
Pointers
- Firestore stores data as collections and documents with rich query support.
- Realtime Database uses JSON trees, offering low latency for live apps.
- Both support offline caching, which improves user experience.
- Built-in rules and identity services support secure scaling.
Supabase (Cloud SQL-like Backend)
Supabase is a Postgres-based backend that gives SQL power while adding realtime sync and APIs. It fits teams that want SQL familiarity but still need cloud sync.
Pointers
- Provides role-level security for strong compliance control.
- Offers APIs, auth, and storage as part of its platform.
- Useful for apps needing both relational strength and realtime channels.
- Easier migration path for teams with SQL background.
Each option solves different problems. SQLite with Drift fits structured offline use. Hive, Isar, and ObjectBox handle local speed. Firestore, Realtime Database, and Supabase support realtime multi-user apps.
| Database Option | Type | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best Fit |
| SQLite / Drift | Relational | Structured queries, joins, offline stability | Needs manual encryption, migrations required | Enterprise apps, analytics, healthcare |
| Hive | Local NoSQL | Lightweight, simple, fast caching | Limited query power | Preference storage, small datasets |
| Isar | Local NoSQL | High speed, indexes, multiplatform | Newer ecosystem | Large offline datasets, retail |
| ObjectBox | Local NoSQL | Built-in sync, ACID, performance | Vendor lock-in risk | Hybrid offline + sync apps |
| Firestore | Cloud NoSQL | Realtime sync, strong SDK support | Costs rise at scale | Chat apps, collaboration tools |
| Realtime Database | Cloud NoSQL | Low latency, simple JSON model | Complex queries, less structure | Gaming, messaging apps |
| Supabase | Cloud SQL | SQL power + realtime channels | Requires backend skills | Fintech, compliance-heavy apps |
Knowing how to choose the right database for Flutter apps helps teams avoid rework and launch with confidence. For implementation, many companies also hire Flutter app developers who can align database choices with long-term scalability and compliance needs.

What performance and security considerations matter when using a flutter database?
A flutter database must balance performance and security. Measure speed, latency, and scale under peak loads. Confirm compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or PDPL depending on region. Verify built-in encryption, authentication, and backup features to protect sensitive customer information from breaches.
Speed, Latency, and Scale
Performance isn’t about raw speed alone; it’s about consistency under load.
- Latency benchmarks: Measure p50 (average) and p95 (worst-case) response times during peak hours.
- Throughput: Evaluate how many read/write operations per second the database sustains without timeouts.
- Concurrency: Test how simultaneous user sessions impact data integrity.
- Scaling: Local options like Drift rely on device resources, while Firestore or Supabase auto-scale with cloud infrastructure.
- Resource impact: Always profile battery consumption and memory usage on Android, iOS, and Flutter web builds.
This level of validation ensures you pick the best database for flutter that won’t collapse under growth.
Compliance in USA, UK, and UAE
Different markets apply different legal pressures, and ignoring them can be costly.
- USA: Healthcare apps must meet HIPAA. Databases need encrypted storage, role-based access, and audit logs. Finance often requires SOC 2 reporting.
- UK: GDPR enforces strict rules on consent, data portability, and cross-border transfers. If your flutter app stores personal data in the cloud, check where servers are located.
- UAE: The PDPL requires businesses to host sensitive datasets locally or get approval for cross-border processing. This directly impacts whether you can use Firebase or must prefer regional providers.
These compliance rules matter when selecting the best database for mobile apps targeting global users.
Security Features
Security must be proactive, not reactive. Every database flutter option has strengths and trade-offs.
- Encryption: Look for AES-256 at rest and TLS in transit. SQLite needs custom encryption layers, while Firestore and Supabase provide defaults.
- Authentication: Managed services integrate with OAuth or SSO. Local databases rely on app-level security only.
- Authorization: Supabase offers Row Level Security (RLS). Firestore rules let you write fine-grained policies. Drift and Hive need custom enforcement.
- Auditing and logging: Cloud options track every request, helpful for GDPR or HIPAA audits. Local storage lacks this visibility.
- Backups and restores: Supabase automates daily snapshots. Firebase offers export tools. Local databases require you to design the strategy.
Testing and checking performance and security features is the most important part of picking the right database for your project.
Performance tests and compliance checks are mandatory. SQLite with Drift excels in offline apps needing structured storage. Hive, Isar, and ObjectBox shine in lightweight apps focused on speed. Firestore and Supabase simplify scaling but demand careful rule design.
Teams that align speed, security, and compliance requirements choose the right flutter database confidently and prevent costly rebuilds.
In a nutshell
The flutter database you rely on will determine how your app performs under real-world pressure. Hive or Isar work best for offline speed. Firebase and Supabase bring realtime sync across devices. SQLite with Drift supports structured records and secure transactions. Making the wrong database decision can lead to rewrites, downtime, and compliance penalties.
Articles like this one give you clarity, but building the right data foundation requires tailored guidance.
At Kody Technolab, we design Flutter apps that handle launch-day traffic, meet strict compliance standards in the USA, UK, and UAE, and scale without painful rebuilds.
Your next step is simple. Let our Flutter specialists review your use case, validate the right database fit, and create a product that grows with your business.
FAQs About Choosing the Right Flutter Database
Q1. What is the best database for Flutter apps?
There is no single best choice. SQLite with Drift works for structured offline apps. Hive, Isar, and ObjectBox fit fast local storage. Firestore, Realtime Database, and Supabase enable realtime multi-user features. The best option depends on your app’s data model and compliance needs.
Q2. Which flutter database options support offline-first apps?
SQLite with Drift, Hive, Isar, and ObjectBox all run directly on the device. These local options let apps function without the internet, store data reliably, and sync later if required. They are often preferred for field apps and retail solutions.
Q3. How do I choose the right database for a Flutter project?
Start with your data type, volume, and performance needs. Decide if you require offline support, realtime sync, or multi-platform support. Test read/write speed, security compliance, and scalability. This structured approach helps avoid rework and costly rebuilds later.
Q4. Is Firebase the best database for mobile apps built with Flutter?
Firebase tools like Firestore and Realtime Database are strong for realtime apps. They provide cross-platform support, offline caching, and built-in security rules. However, they may create vendor lock-in and higher costs at scale. Always compare against open-source or SQL options.
Q5. Do Flutter databases meet compliance requirements in the USA, UK, or UAE?
Yes, but it depends on the provider and configuration. For healthcare or finance apps in the USA, HIPAA or SOC 2 must be met. In the UK, GDPR is critical. In the UAE, PDPL regulates local data hosting. Always verify before launch.
Q6. Can one flutter database work across Android, iOS, and web?
Yes. Options like Firestore and Supabase support all three platforms through SDKs. Isar and Hive offer limited web support. SQLite needs wrappers for browser-based apps. Always confirm web parity if your project targets Flutter web or desktop.
Q7. When should businesses hire Flutter app developers for database integration?
Hire Flutter app developers when you need tailored database architecture, complex integrations, or compliance-driven builds. Skilled developers design secure schemas, manage sync strategies, and optimize performance across platforms. This ensures your app scales without technical debt or compliance risks.













 Contact Information
Contact Information