Every second, data is flying in from apps, sensors, clicks, and customer actions. And businesses are done just watching it pile up. A new world has begun where reacting is not fast enough; anticipating sets the stakes for what it takes to succeed. This is where the transition, predictive analytics vs traditional analytics, becomes a game-changing scenario.
Traditional analytics tell you what happened. Predictive analytics tells you what is going to happen. And that difference can mean everything. Companies concerned with how their customers will behave in the future have been using this method to achieve speed, intelligence, and advantage along their supply chains.
And that momentum is impossible to overlook.
The predictive analytics market, valued at $5.29 billion last 2020, is going to touch $41.52 billion by 2028. (statista)
That is not just impressive growth, but proof that predictive tools are already starting to be a central part of modern businesses to drive results.
In the sections ahead, we’ll explore how predictive analytics compares to traditional approaches, highlighting where it’s making the biggest impact, and show you how to start using it in your own business to stay ahead of the curve.
Let’s dive in.
The Evolution of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics has taken a longer and quieter journey from a niche tool to a core business competency. This transformation usually occurred through data experts using complex statistical modeling strategies and working with limited data. It was very powerful but too slow, often liable to be disregarded by most teams. Things have changed over the years with the advent of technology. Cloud computing facilitated data accessibility, while machine learning enhanced predictive accuracy. Now, with real-time data streaming in every direction, the speed and accuracy of predictive insights have proven to be stellar. A well-structured Predictive Analytics Guide today goes far beyond forecasting outcomes. It helps businesses make better real-time decisions powered by conviction and clarity.
Understanding the Big Picture of Analytics
Before we compare traditional and predictive analytics, we need to understand the bigger picture. Not all analytics are designed to do the same thing. Some focus on explaining the past, while others help you plan for the future or decide what actions to take.
That’s why businesses use different types of analytics depending on what they’re trying to solve. Whether you’re analysing performance, uncovering the root of a problem, predicting outcomes, or deciding your next move, each type has a specific role.
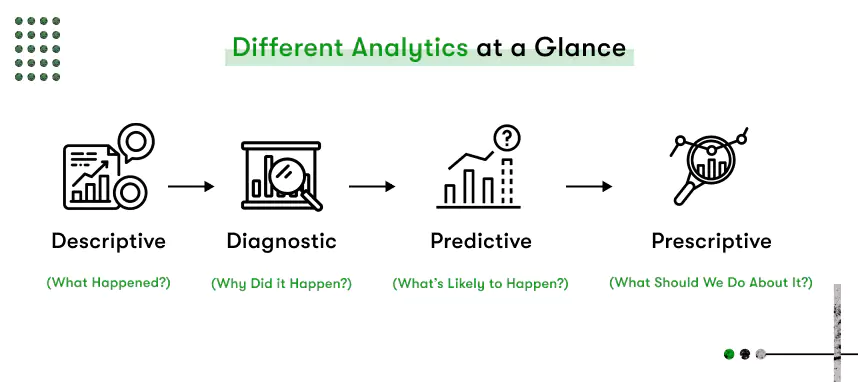
Breaking Down the Four Types of Analytics
Getting familiar with the four main types of analytics will give you the foundation you need to make smarter, more informed decisions. Especially if you’re considering predictive analytics consulting, knowing where predictive fits in is a great place to start.
Descriptive Analytics
This is your starting point. Descriptive analytics looks at historical data to give you a clear picture of past performance. Think reports, dashboards, and summaries. For example, sales reports showing revenue by quarter fall under this category. It’s all about the “what.”
Diagnostic Analytics
Once you know what happened, the natural next question is why. Diagnostic analytics digs deeper to uncover root causes. Say your sales dropped in Q3; diagnostic tools help you pinpoint whether it was due to a pricing change, reduced marketing, or seasonal trends.
Predictive Analytics
Here’s where things get exciting. AI in Predictive Analytics uses machine learning, statistical models, and historical data to forecast future trends. It doesn’t just stop at what or why; it tells you what might happen next. For instance, predicting which customers are likely to churn or what inventory levels you’ll need next month.
This is where the real contrast between predictive analytics vs traditional analytics examples becomes clear. Traditional methods tell you where you’ve been. Predictive analytics strategy for non-tech teams helps you plan where to go.
Prescriptive Analytics
The most advanced type, prescriptive analytics, doesn’t just predict; it recommends actions. Using AI and advanced algorithms, it suggests the best course of action to achieve specific outcomes. It’s like having a data-powered advisor by your side, guiding decision-making in real time.
Placing It Together
Descriptive ➝ Diagnostic ➝ Predictive ➝ Prescriptive
Every step of ascending adds another level of depth, which is part of making that fugue out of just the mere frame of reference of past to bottom of dreaming about the future with certainty.
When comparing predictive analytics vs traditional analytics examples, this flow shows how businesses evolve in their data maturity. Traditional analytics (descriptive and diagnostic) tells you what happened and why. Predictive analytics and beyond help you shape what’s next.
What is Traditional Analytics?
Traditional analytics are the foundation of how businesses have understood data for decades. It mainly includes descriptive and diagnostic analytics, which means that it is all backward to understand what happened and why it happened.
Traditional analytics concern themselves with performance, trends, and harnessing historical information to diagnose problems. Not predictions about the future, but understanding what happened so companies can learn from it.
Common Uses
You have probably seen traditional analytics more often in action. Some specific business applications include:
- Monthly or quarterly sales report
- Website traffic analysis
- Customer service problem tracking
- Inventory assessment
- Marketing campaign performance review
In short, if you ask, “How did you last month?” Like drawing data to answer questions, are you pulling data? Or “Why has our conversion rate fallen?” You are working within the traditional analytics world.
Tools Used in Traditional Analytics
Many businesses are accustomed to using the following traditional analytic tools:
- Excel and spreadsheets
- Business intelligence such as Tableau or Power BI
- SQL databases
- Google Analytics as web performance measurement
These tools help visualise and explore what’s already happened. But they stop short of predicting what’s coming next, and that’s where the difference between traditional analytics and predictive analytics becomes a game-changer.
What is Predictive Analytics?
Now let’s flip the script.
Predictive analytics center on the future. Instead of analysing last year’s data, it uses patterns and predictive analytics trends; it has the capability of forecasting future outcomes with computer programs that provide advanced algorithms. The organisations are thus moving from a reactionary to an actively managed decision-making.
Imagine knowing which customers are likely to leave before they do, which products will trend next quarter, or when a machine is likely to break down. That’s predictive analytics at work.
How Predictive Analytics Works?
Predicative analytics isn’t just a statement for interpretation but involves data mining, statistical modeling, and machine learning to infer well-founded guesses about what’s likely to take place. It’s not like saying “Sales have dipped the previous month,” but in this case, it will say, “Sales will possibly decrease next month as well if you don’t take action.”
This is the key difference between traditional analytics and predictive analytics: traditional helps you understand what was, while predictive helps you prepare for what could be.
That’s the difference between the old analytics and how predictive analytics works; The first would learn about what was, and the next one would prepare itself for what could happen.
Why It Matters for Modern Business?
The beauty of future analytics is that it gives leaders the right to make clever, fast decisions before the problem. In an era where one step ahead can mean everything, such foresight is not just good – this is necessary. Whether it is reducing the risk, adaptation of resources, or increasing the satisfaction of customers, future analytics opens the doors that traditional analytics cannot simply do.
How Different Analytics Have Different Results In The Same Situation?
Use Case: Online Retail Store Facing a Drop in Sales
Your eCommerce company notices that monthly revenue has dipped. You want to understand why, what went wrong, and how to fix it. This scenario highlights key predictive analytics use cases, showcasing detailed predictive analytics vs traditional analytics examples and clarifying the difference between traditional analytics and predictive analytics.
1. Descriptive Analytics: What happened?
Input:
- Sales data from the last 6 months
- Website traffic reports
Output/ Result:
- Revenue dropped by 18% in the last two months.
- Product category “Electronics” saw the largest decline.
- Website traffic from mobile phones has been going down.
Result to Show: There is a need to deal with the decline and take away some improving areas delineated by these scenarios.
2. Diagnostic Analytics: Why did it happen?
Input:
- User behavior analytics
- Conversion funnel drop-off
- Mobile site performance
Output/ Result:
- Mobile bounce rate increased due to longer page load times.
- Negative reviews on certain electronic products are negatively affecting them.
- Competitor offering a sale during that period.
Result: Identified reasons behind the sales drop (site performance, product perception, and competition).
3. Predictive Analytics: What are the probabilities of things occurring?
Input:
- Former trends of sales
- Seasonal demands data
- Past purchases and buying behavior by customers
Output/ Result:
- In fact, sales will plummet a further 10% within the coming month, without any actions taken.
- 60% of churn chances of loyal customers as a result of a negative experience.
Result: Predicted losses to be indexed for upcoming events, also called risk to customers.

4. Prescriptive Analytics: What should we do?
Input:
- Predictive model outcomes
- Inventory and marketing data
- Optimisation algorithms
Output/ Result:
- Improve the speed of the mobile site
- Provide target discounts on top-reviewed electronic items
- Start a campaign for cart abandoners
- Estimated recovery: 12-15% increase in sales next month when implemented.
Results: Actionable strategy to fix sales and reduce churning.
Summary of how different analytics give different results, and what is the core difference between traditional analytics and predictive analytics?
| Analytics category | Question Answered | Tools Used | Result |
| Descriptive | What has happened till now? | Dashboards, reports | Shows drop in sales and traffic |
| Diagnostic | Why did it happen? | Funnel analysis, A/B testing | Pinpoints mobile performance and the current competition |
| Predictive | What is likely to happen next? | Forecast models, ML | A decrease in projects highlighting concerns of churn |
| Prescriptive | Ideally, what needs to be done? | AI/ML, optimisation | Recommends campaigns, fixes, and promotions |
Predictive vs Traditional Analytics. Why Do We Need Predictive Analytics If We Have Traditional Analytics?

It’s a fair question: if traditional analytics already helps us understand performance and troubleshoot issues, why do we need predictive analytics?
The answer is simple: in today’s hyper-competitive, fast-moving business landscape, understanding the past isn’t enough. You need to anticipate what’s coming next and act before problems (or opportunities) arrive.
Here’s why more and more businesses are choosing predictive analytics vs traditional analytics, and why that shift matters.
1. Traditional Analytics Predicts the Past and Not the Future
The very first reason for predictive vs traditional analytics is that Traditional analytics tell you how and when things happened, and once you find that out, you’re left asking, “So what do we do next?”
That’s where predictive analytics come in to help with the answers. It converts historical data into practically a crystal ball. It can assist you in answering questions like:
- Which type of customers are most likely to churn next month?
- How will demand change in the following quarter?
- What is the risk of disruption to my supply chain?
This forward-looking point of view is one that traditional methods cannot offer.
2. The Business World Has to Be More Proactive Than Reactive
Let’s face it, even after your revenue or customer base is affected, this is not a good picture. Predictive Analytics allows you to make a well-informed decision before catching warnings and increasing problems.
Rather than waiting for sales to fall or customers to complain, predictive tools allow you to anticipate trends and act ahead of the curve. However, despite their advantages, one of the biggest Predictive Analytics Challenges lies in building models that remain accurate across shifting customer behaviors and volatile market dynamics. This is something traditional analytics often fail to address in real-world use.
3. Gain Competitive Advantage
In industries where time, customer behavior and market trends quickly shift, the business that uses future analytics gains a serious lead.
While considering predictive vs traditional analytics, with Predictive analytics, they can:
- Launch the right product at the right time.
- Customise the experience for customers based on likely behavior.
- Refine pricing strategies using demand forecasting.
Traditional analytics might state what has happened, but predictive analytics allow these businesses to maneuver faster than their competition.
4. Improved resource planning and risk management
In predictive vs traditional analytics, Predictive Analytics makes it possible for companies to better allocate funds, whether it be toward a budget, staff, inventory management, marketing expenses, and so on.
It has an essential role in managing the risk, before they flag the potential hazards before they become expensive problems. Think about the detection of fraud in finance, equipment failure in manufacturing or delay in the supply chain in logistics.
This is the place where the difference between traditional analytics and predictive analytics exceeds just theory – it affects direct profits, efficiency and flexibility.
5. Enables AI & Automation
In predictive vs traditional analytics, predictive analytics is the entrance to automation and AI-powered decision making. With AI & machine learning in predictive analytics, your system can not only estimate future results, it can also start automating the reactions – adjusting inventory levels, sending target customer messages, or even triggering maintenance alerts without human intervention.
Traditional analytics supports reporting. Predictive analytics enables intelligent action.
When to Use What?
Not every situation calls for future analysis, and traditional analytics still play an important role in many business decisions. Here is a side-by-side breakdown that helps you decide which approach is best based on your needs and goals.
A detailed comparison of Predictive Analytics vs Traditional Analytics
| Factor | Traditional Analytics | Predictive Analytics |
| Business Objective | Understand past performance and root causes | Forecast future trends and drive proactive decisions |
| Data Maturity | Works with basic historical data | Requires structured, high-quality historical and real-time data |
| Infrastructure | Can run on spreadsheets and BI tools | Needs scalable computing, storage, and advanced platforms |
| Skills Required | Analysts or business users with basic data skills | Data scientists, analysts with ML/statistics expertise |
| Accuracy vs Actionability | High accuracy on what already happened | High value in shaping outcomes, though predictions vary |
| Real-Time Decisions | Not ideal. More reactive than real-time | Great for live forecasting and adaptive systems |
| Continuous Learning | Static insights.Doesn’t learn over time | Improves with more data. Models evolve and self-optimize based on data |
| Cost & ROI | Less upfront cost with quick insights | Higher investment, but long-term ROI of Predictive Analytics is significant |
| Automation & AI Integration | Limited to manual interpretation | Enables automated, intelligent decision-making systems |
How are different industries using future analytics to move forward?
Predictive Analytics is explaining how industries are operated, not in principle, but in behavior. Here is a quick look at how different areas are putting it to work:
- eCommerce: You can predict customer behavior, personalise product recommendations, and forecast trends in sales.
- Travel: Booking trends can be anticipated, prices can be better ranged, and personalised experiences can be designed.
- Healthcare: Predictions about the results of patients, decreased value of readmission, and optimisation of hospital resources.
- Fintech: Detect fraud while it happens, assess credit risk, and personalise financial products.
- Logistics: Appropriate inventory management, overcoming delivery delay, and demand forecasting.
- Distribution services: to increase the route plan, estimate the distribution time and control the efficiency of the fleet.
In addition, from smarter marketing to more active operations, future-stating analytics is allowing these areas to work rapidly, plan accurately, and actually distribute. This shift is delivering a clear ROI of Predictive Analytics.
Final Words
The business landscape, in fact, is changing quite fast. Conventional analytics give you a good rearview mirror; predictive analytics provide the headlights, shining a light on what is coming down, helping you plan your route even before the turns appear. A solid Predictive Analytics Consulting approach helps businesses anticipate trends, respond faster, and make better decisions. It is now a competitive necessity in every field, from eCommerce and healthcare to logistics and fintech.
The best part? Almost nothing has to change at once. Start small and smart, but start where it matters most.












 Contact Information
Contact Information